GIS 5100 Module 2
In this weeks module, LiDAR data is used and converted using several different methods to obtain information about tree height and canopy density in a grid section of Shenandoah, VA. Data transformation methods and tools include Minus, LAS to MultiPoint, IS NULL, Con, Plus, Divide, and data to raster tools for different data types. The input data is a LAS grid of Shenandoah obtained from Virginia LiDAR, and the outputs are raster datasets showing tree height, surface elevation, and canopy elevation.
The following tools are used to determine tree height:
The Minus tool is used to determine the difference in feature height from elevation and ground surface features which is useful in determining tree height.
The following tools are detailed as they are used to determine the biomass density of the grid patch.
LAS to Multipoint converts the LAS into a format more useful to analytics. This is performed on both the surface and vegetation datasets. IS NULL is used to identify those features which do not have a value, and Con tool assigns a value to them, and is performed for both the surface and vegetation datasets. The Plus tool is used to combine the results of the surface and ground datasets. The Divide tool is used to perform a calculation across multiple spatial datasets and determine the density of the canopy.
 |
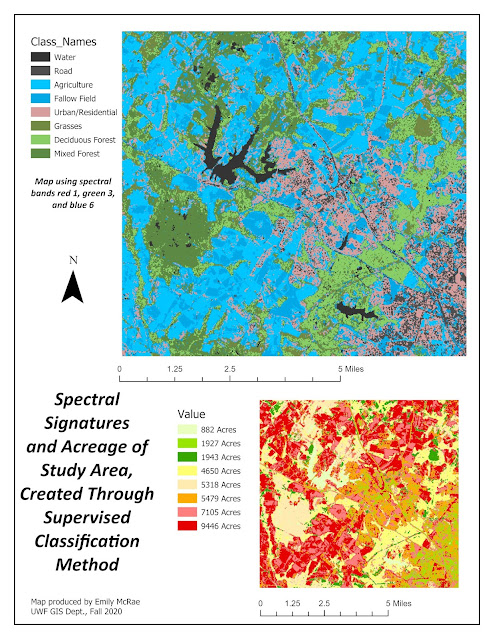
| Map shows canopy cover and tree height in grid patch, with a graph of tree height variation. |



Comments
Post a Comment